Age Spot, Pigmentation & Sun damage
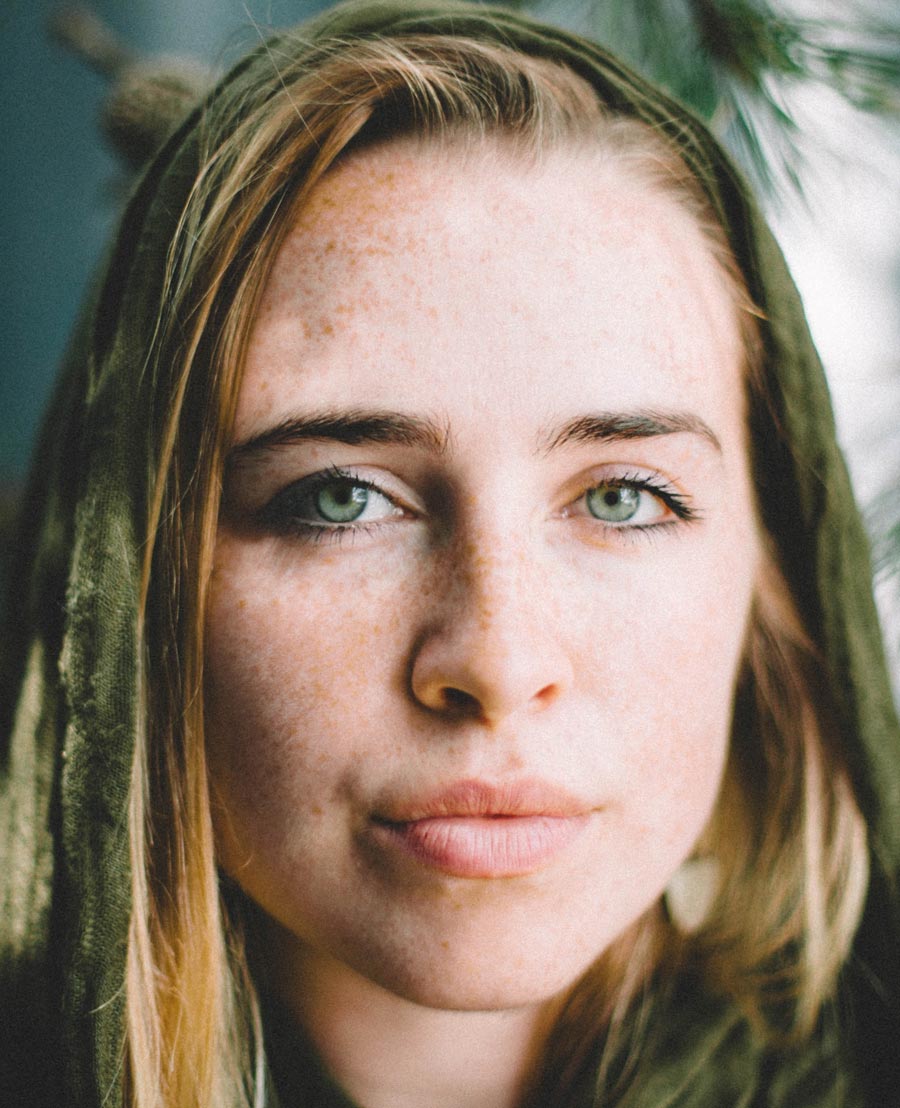
Uneven pigmentation of the skin and hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition that can appear on your face, hands, decolletage and other parts of the body that are exposed regularly to the sun.
Age spots and sun spots form when the pigment clumps or is produced in high concentrations. These are usually not dangerous to you but can be of cosmetic concern. At FaceRestoration our surgeons are able to offer advice and treatment options as well as screen and monitor for progression to more dangerous cancerous lesions.
ABOUT THIS CONDITION
INFORMATION ABOUT YOUR SYMPTOMS
Pigmentation refers to the colouring of your skin, where hyperpigmentation is the term used to describe increased areas of uneven pigmentation. Skin cells called melanocytes produce melanin which is responsible for your skin’s colour. Hyperpigmentation can appear as clumps known as age spots or sun spots, or more widespread as melasma, often related to hormonal changes, and following inflammation or local skin trauma as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), which can occur in all skin types but tends to affect those with darker skin types more.
We are able to monitor pigmentation and sun damage objectively with lesion mapping and VISIA skin analysis. Solar lentigines or age spots are harmless but may resemble more serious conditions, such as moles, lentigo maligna, melanoma and solar keratosis. Medical grade skin care can help reduce pigmentation, and sun damage. We can advise regarding appropriate SPF applications and types suitable for you.
What is Sun Damage?
What is Post-inflammatory Hyperpigmentation?
What is Melasma?
What are Age Spots?
How can I prevent pigmentation?
- Avoid the sun between 10am and 3 pm when the sun’s rays are the most intense
- Wear water resistant sunscreen every day. It should have a sun protection factor (SPF) rating of at least 30 and contain both UVA and UVB protection
- Use a sunblock on your lips. Choose a product that has been specially formulated for the lips with a sun protection factor of 20 or more.
- Apply sunscreen at least 30 minutes before sun exposure. Reapply every two hours, and more often if swimming or perspiring.
- Wear protective clothing such as hats, long trousers and long sleeved shirts. These help to protect your skin from UV rays. For the best protection, wear UV-blocking clothes with an ultraviolet protection factor (UPF) of at least 40
- Wear sunglasses with UVA and UVB protection to protect the delicate periocular skin which is more prone to sun ageing, and the eye.
What if my skin condition looks suspicious?
For areas of pigmentation or sun damage that are suspicious we may recommend a biopsy to allow us to exclude any cancerous lesions such as melanoma, lentigo maligna, Bowenoid actinic keratosis, basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma. Some medical treatments can be used for precancerous lesions. When cancer is confirmed we will be able to resect and reconstruct with our ScarslessTM program. We work with a multidisciplinary team of pathologists and dermatologists to offer you a safe and seamless service and have particular expertise in the surgical treatment of skin cancer around the periocular area.
Related conditions
Similar conditions clients also view
-

Jawline & Jowls & Double Chin
-

Nose Enhancements
-

Dry Eyes & Blepharitis
-

Eyelash Loss & Short Eyelashes
-

Tyndal Effect
-

Rosacea, Acne & Acne scars
-

Dermatochalasis (Loose Skin) & Hooded Eyes
-

Cosmetic Eyelid Surgery
-

Chalazion & Stye
-

Filler Related Complications & Vascular Occlusion & Vision Loss
-

Thin Lips
-

Scars, Keloid Scarring & Scar Management


How we can help
Contact us for a consultation

Booking with us
Arrange a consultation with us using the button below at a time of your choosing. This may be held through video chat dependant on COVID guidelines at the time.

Your consultation
We will then discuss with you your symptoms and advise you on how best to proceed with helpful guidance on treatments through our expert knowledge and training.

Treatment after care
Once an appointment has been arranged, we will then begin treatment and support you along the process, including specialised aftercare.